The article provides an overview of Mitigating Controls in SAP GRC, their creation and usage in the whole GRC ecosystem. There is a special focus on both Access Control and Process Control modules, comparing the operative differences and impact in each of them.
During this article we are going to review the topic of Mitigating Control within an SAP GRC environment.
SAP GRC
SAP GRC is a solution provided by SAP that helps an Organization to reduce Risks, provide information for decision making and increase efficiency by automation:
The SAP GRC Area comprises different modules, please find below the most important ones:
When it comes to Mitigating Controls, you can maintain them inside two different Modules: Access Control & Process Control. However, the maintenance of Mitigating Controls is different on each of them.
SAP® GRC Access Control
This module is focused on the technical area of User and Role Management. As a summary, the tools provided by Access Control module are:
- Access Risk Analysis (ARA) – that helps to define and monitor access Risks within a system.
- Access Request Management (ARM) – that helps to define and execute the User Provisioning process in a system.
- Emergency Access Management (EAM) – that helps to define and execute the Emergency Access Provisioning process in an SAP® system.
- Business Role Management (BRM) – that helps to define and execute the Role Management process in an SAP® system
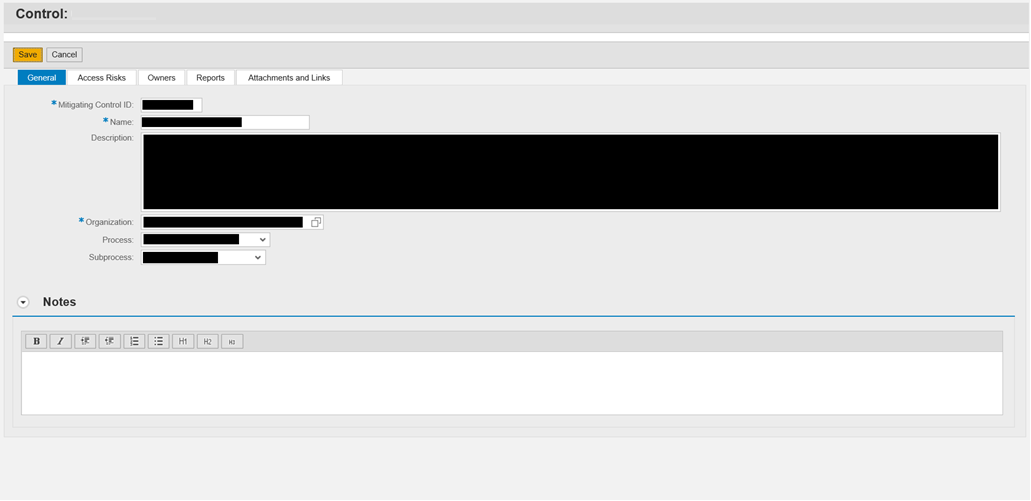
The first module, Access Risk Analysis (ARA) is the one that manages the definition and usage of Mitigating Controls. Please find below one screenshot that shows the different fields that are required for the creation of a Mitigating Control:
- Mitigating Control ID: the ID that will identify the Mitigating Control that is being created.
- Name: short description that will be included inside the Mitigating Control.
- Description: long description that will give all the information about the Mitigating Control.
- Organization: the scope where the Mitigating Control is applicable.
- Process: Business Process where the Mitigating Control belong.
- Subprocess: Subprocess where the Mitigating Control belong.
Apart from the first Tab (“General”), the Mitigating Control has 4 more Tabs:
- Access Risk: Inside this tab is where you set the Access Risks to which this Mitigating Control is applicable.
- Owners: Here you are required to include an Owner for the Mitigating Control, who will be accountable for the Mitigating Control Periodic Review.
- Reports: Documentation tab.
- Attachments and Links: Here you can upload documents with more information about the Mitigating Control (or refer it to a specific site).
Once we understand what is the information that is being included as part of the Mitigating Control definition, it is important to know what we can do with this inside SAP GRC Access Control Module.
Mitigating Controls are being used mainly inside ARA, ARM and BRM modules. Let’s try to establish what we can do in each of them.
Access Risk Analysis
Mitigating Controls can be assigned to a specific user or role, and this will mitigate it. It is important to understand that each Mitigating Control will be applicable only when the Risks that were selected inside the Master Data appear. You cannot mitigate a Risk if there is no Mitigating Control linked to it. Once we perform the Mitigation to the User/Role, it will be excluded from the Risk Analysis (only for Risks to which you assigned a Mitigating Control; if you did not mitigate a Risk, the User/Role will still show up for that Risk).
Access Request Management (ARM)
When executing the User Provisioning Process, you can assign a Mitigating Control to a User prior to the real assignment inside the system. This will help to identify those Risks that were reviewed and approved.
On the other side, there is a specific periodic review of Mitigating Controls inside the ARM tool. This will help to review the Master Data of Mitigating Controls on a periodic basis, to ensure that everything is up to date.
Business Role Management (BRM)
Like the previous case of ARM module, when executing the Role Provisioning process, you can assign a mitigating control to a Role that is going to be promoted to the Production system. It is important to note that when performing Role Mitigation this will be extended to all Users that currently have the Role assigned inside the SAP system.
SAP GRC Process Control
The SAP GRC Process Control module is different from the SAP GRC Access Control module since it does not only keep documentation but also performs monitoring operations inside the SAP System.
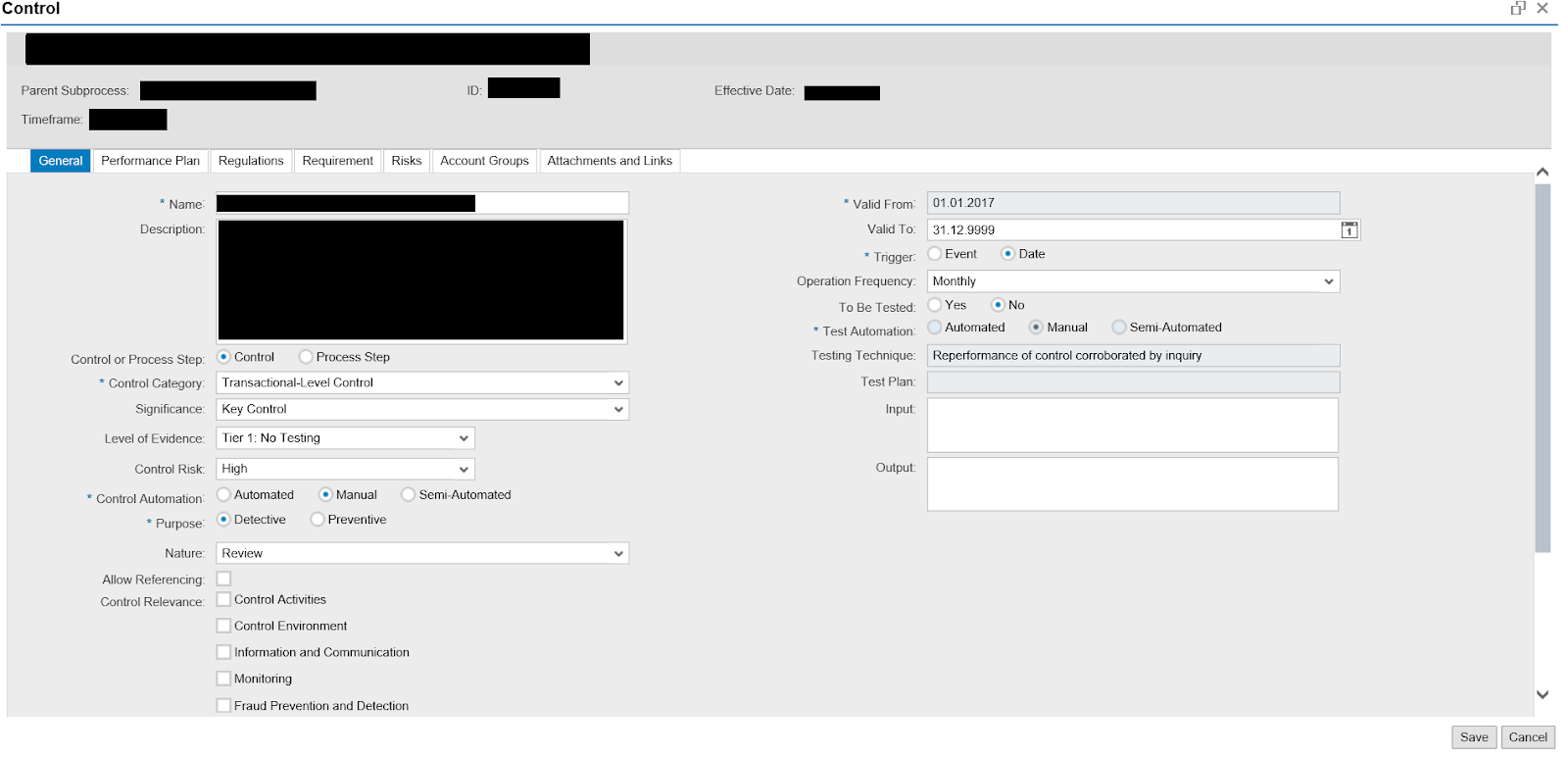
The Master Data for the Mitigating Controls is a lot more detailed than the example we reviewed inside the SAP GRC Access Control Module:
The main differences are:
- Control Automation: defines if the Control is automated, semi-automated or manual.
- Level of Evidence: defines if the Control needs to be tested.
- Purpose: states if the Control is Preventive or Detective.
Furthermore, the following Tabs are Key for the Master Data definition:
- Regulation: establish the Regulation where the Mitigating Control is applicable.
- Risk: establish the Risk that can emerge if the Control is not working as expected.
- Performance Plan: establish the test steps and the responsible for each of them when performing the testing of the Control.
- Attachment and Links: upload all the information related to the Mitigating Control that will be sent to the responsible when testing the control.
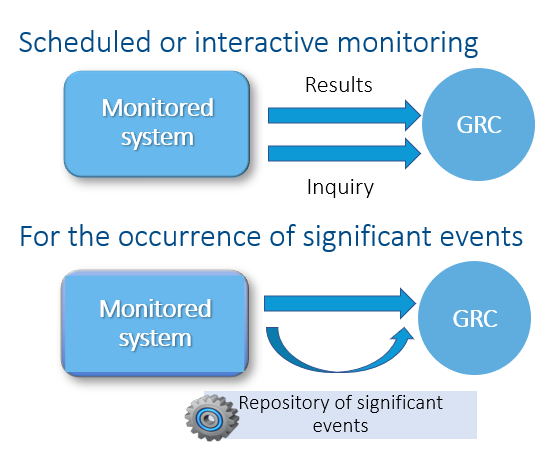
There are two types of operation that the Process Control system can perform:
So, as we stated before, the Process Control system can perform operations to verify if the Controls are working as expected inside the system.
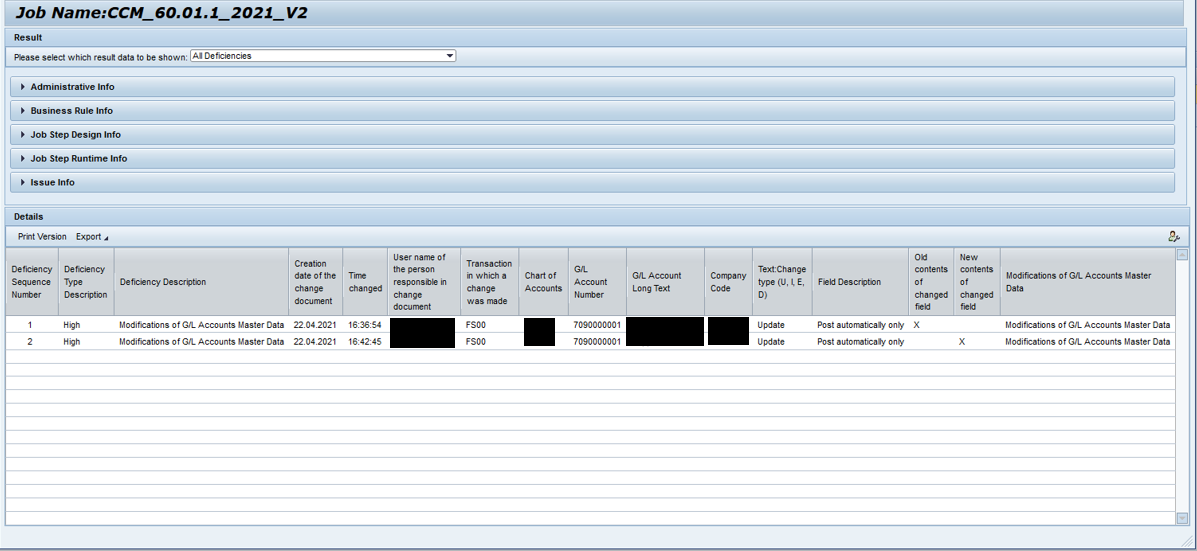
The following image detects all the GL Accounts that are created within an SAP system and identifies the person who created it. Furthermore, as we discussed previously, the advantage of Process Control is the ability to perform monitoring activities to ensure that everything is aligned with the Organization Policies.
As a conclusion, SAP GRC Access Control module helps Organizations to document Mitigating Controls and use them for Access Risks only. However, SAP GRC Process Control module provides more capabilities that excel in automating Mitigating Controls and identifying deficiencies that do not comply with the Mitigating Control description.