Do you have a SAP GRC Process Control license and are you still not taking full advantage of the potential of Manual Control Performance?
Many organizations still execute their controls—both business process and IT controls—in a manual, fragmented, and inefficient way. These controls, which in many cases directly impact business continuity, are managed through multiple channels such as emails, Microsoft Teams, or other non-integrated tools. This creates a strong dependency on individuals to consolidate and validate information, resulting in data that is difficult to access, hard to trace, and highly prone to errors.
It is essential to eliminate the manual execution of these processes and ensure that each control is properly aligned with the process executor and the control owner.
The solution lies in operating under an Integrated Global Control Framework, centralized in SAP GRC Process Control, enabling the automation and orchestration of control execution across both SAP and Non-SAP systems. This not only reduces operational risk and the time spent on repetitive tasks, but also provides greater visibility for senior management and clearer accountability in control management.
Key Features and Benefits
Implementing all controls—both SAP and Non-SAP—within SAP GRC Process Control allows organizations to centralize management in a single tool, transforming how controls are monitored, executed, and audited.
Main MCP Features
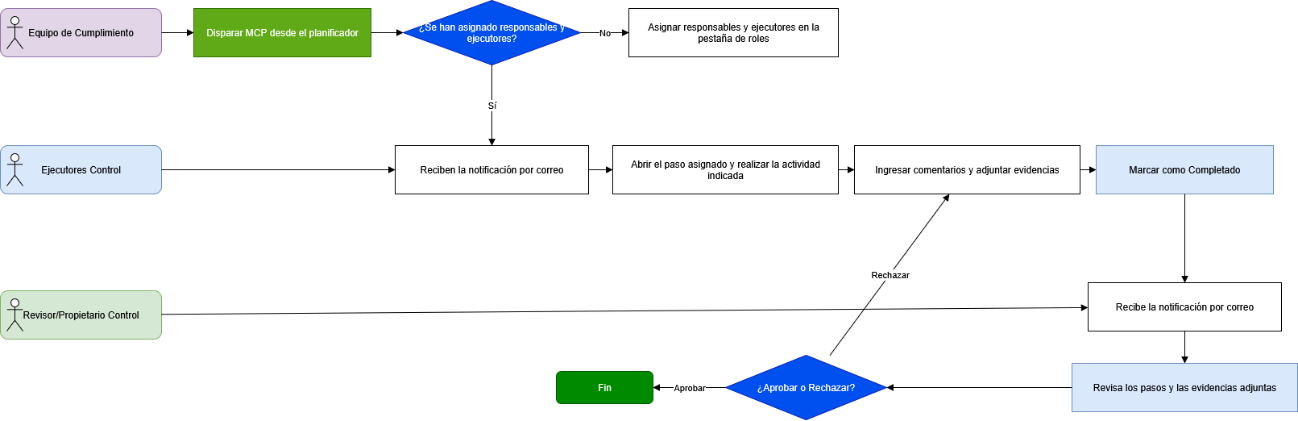
- Structured planning: Definition of performance plans with sequential steps, durations, and clearly assigned responsibilities.
- Flexible role assignment: Support for multiple executors and optional review by the control owner.
- Evidence and comments management: Ability to attach documentation and observations at each step.
- Deadline control and alerts: Step-level tracking with due dates and prioritization of critical tasks.
- Review and approval/rejection: Robust workflow with rework options in case of rejection.
- End-to-end monitoring and traceability: Real-time status, action logs, and audit-ready evidence.
- Incident management integration: Registration and tracking of deviations within the same framework.
- Applicable to SAP and Non-SAP: Orchestrates manual controls regardless of the source system.
An example of a possible control execution flow in MCP could be:
In addition, using SAP GRC Process Control as a central control repository provides key capabilities that enhance governance:
- Control matrix with attributes that facilitate classification and analysis.
- Efficient execution tracking by entity, with clear traceability.
- Centralized management, eliminating fragmented tools and channels.
- Intuitive interface that simplifies the experience for executors and control owners.
- Real-time and historical reporting, enabling trend analysis and informed decision-making.
- Immediate availability of evidence, accelerating audits and internal reviews.
These capabilities translate into tangible benefits for the organization:
- Reduction of operational costs: By minimizing compliance risks and avoiding corrective audits.
- Prevention of penalties: Through more efficient and well-documented regulatory compliance.
- Increased operational efficiency: Continuous monitoring enables early detection and correction of deviations.
- Improved return on investment (ROI): Savings in personnel costs and protection of business value by avoiding critical risks.
- Scalability: Ability to manage an unlimited number of controls, adapting to organizational evolution within a centralized and automated environment.
In addition to the following intangible benefits gained by using SAP GRC Process Control as a tool:
| Strategic Dimension | Focus | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Strengthened Regulatory Compliance | Integration and coordination of control efforts within a single platform, facilitating regulatory and corporate compliance. | – Full traceability of controls and evidence. – Stronger audit readiness. – Alignment with regulatory frameworks (SOX, GDPR, etc.). – Reduction of errors caused by manual execution. |
| Proactive Management of Critical Risks | Implementation of a structured framework to identify, assess, and mitigate operational and financial risks in a unified manner. | – Early mitigation of material risks. – Risk-oriented control design. – Reduction of audit findings. – Improved data-driven decision-making. |
| Operational Optimization and Standardization | Clear and consistent structure that simplifies control execution and improves organizational efficiency. | – Standardization of control processes. – Elimination of duplicate and manual tasks. – Improved cross-functional collaboration. – Scalability and ease of maintenance. |
Conclusion
Manual Control Performance (MCP) in SAP GRC Process Control transforms the management of manual controls by eliminating tool fragmentation and improving traceability. It enables the definition of plans with sequential steps, role assignment, deadline control, and evidence management—all within a structured workflow.
In summary, MCP delivers:
- Full visibility and traceability.
- Reduced costs and risks through standardized processes.
- Improved risk management through planning and monitoring.
- Resource optimization by eliminating manual tasks.
- Robust regulatory compliance with frameworks such as SOX or GDPR.
Therefore, organizations that already hold a SAP GRC Process Control license have a strategic opportunity in MCP to transform their control model, align it with corporate governance best practices, and strengthen their operations against risks and regulatory changes.