Active Directory (AD) is often the main source of user information within a company. Therefore, its integration with SAP® GRC should be an essential practice to ensure centralized, secure, and efficient user data management in enterprise environments. By establishing Active Directory as the main user data source for SAP®, organizations can reduce manual errors, automate provisioning processes, and ensure that the information is always synchronized and up-to-date.
In this step-by-step guide, we will explore how to properly configure the communication between Active Directory and SAP® GRC, from defining RFC connections and LDAP configuration, to executing full user synchronization. You will also learn how to set AD as the master data source and prevent unwanted manual modifications in the SAP system.
Steps to Connect Active Directory with SAP® GRC
- RFC communication.
- LDAP configuration.
- GRC synchronization.
RFC Communication
Communication between Active Directory and SAP® GRC requires the definition of a TCP/IP Connection. The key fields of this connection are:
- Gateway Host
- Gateway Service
- Registered Program ID
Both Gateway Host and Gateway Service are exclusively related to the GRC system. The Registered Program ID must have the same name as the RFC connection. It is important to note that there may be issues when registering the Program ID if the gateway has registration restrictions.
LDAP Configuration
The next step is to connect to the LDAP server, which is configured through the LDAP transaction in SAP®.
Key fields:
- Host Name
- Port Number
- Base Entry
- System Logon
SAP® provides a default mapping for Active Directory, which can be applied by pressing “F8”. Contact your System Administration team to confirm that the Active Directory mapping is correct. In addition, a user that already exists in Active Directory must be defined for the connection. This configuration is done under the “System Users” option.
Remember to include the Base Entry to locate the System User within Active Directory.
Once the LDAP server is configured, you must define an LDAP connector.
The name of the connector MUST match the RFC connector name.
The naming convention for the LDAP connector is:
Gateway Host_SID of the GRC system_Gateway Service Instance Number
Example: SAPGRC00_GRP_00
Then, this LDAP connector must be activated.
Common issues when activating the LDAP connector:
- The Registered Program ID in transaction SM59 was not registered.
- The Gateway Host and Gateway Service in SM59 are incorrect.
- The LDAP library is missing in the SAP® GRC system and must be installed.
Once the LDAP connector is active, you can run the “Connection Test” for the TCP/IP Connection in the SM59 transaction:
GRC Synchronization
After completing the above tasks, a synchronization operation is required to establish Active Directory as a User Data Source.
Steps:
1 Verify that all previous configurations are correct.
2 Execute the LDAP transaction and press “Log On”:
3 Once connected, press the “Find” button:
Use the following expressions to find the SAP User ID:
(&(samaccountname=SAP_USER_ID))
(&(mail=mail_address))
On the GRC side, do the following:
- Define the LDAP Connector Group using the SPRO transaction:
Maintain Connectors and Connection Types - Assign the LDAP Connector to the “PROV” and “AUTH” scenarios using SPRO:
Maintain Connection Settings
Then, run the SAP RSLDAPSYNC_USER program using transaction SE38, including the previously defined LDAP Server and Connector. You can search for a specific user, but it is recommended to test the full search.
If you want to create all Active Directory records inside SAP®, make sure to enable that option.
Finally, execute the GRAC_REPOSITORY_OBJECT_SYNC program to perform the Full Synchronization (Full Sync Mode) using the LDAP Connector.
Set Active Directory as the Main User Data Source
After the integration, it is essential to configure Active Directory as the Main User Data Source in SAP® GRC using the SPRO transaction:
- Maintain Data Sources Configuration
Then, include Active Directory as:
- User Search Data Source
- User Detail Data Source
Next, the field mapping between Active Directory and SAP® fields must be done using:
- Maintain Mapping for Actions and Connector Groups
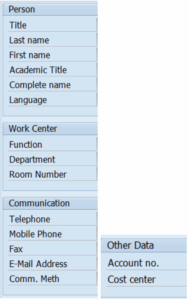
It is suggested to map as many relevant fields as possible, especially those used in the SU01 transaction, such as:
- USERID → SAMACCOUNTNAME
- LASTNAME → SN
- FIRSTNAME → givenName
- FUNCTION → title
- DEPARTMENT → Department
- TELEPHONE → telephoneNumber
- TELNUMBER → mobile
- EMAIL → MAIL
- PERSONNEL_NUMBER → employeeID
- MANAGERID → manager
- LOCATION → country
- COMPANY → company
These fields can also be used for the definition of User Defaults, such as:
- Logon Language
- Decimal Notation
- Date Format
If there is a requirement to use a specific field from Active Directory within SAP® GRC, you can create a Custom Field and map it also using:
- Maintain Mapping for Actions and Connector Groups
Restrict Manual Changes
To avoid undesired modifications, it is recommended to restrict manual changes in the fields that are pulled from Active Directory. This configuration is done via the SPRO transaction:
- Maintain End User Personalization
This option allows all fields that are populated from Active Directory to be set as non-editable by end users.
Need Help with Active Directory and SAP® Integration?
If you found this article helpful or are considering implementing Active Directory as a User Data Source in SAP® GRC, we are here to support you. Our team of experts can guide you throughout the process, from initial setup to optimizing synchronization and access control.
Contact us here, or visit our SAP® Security and SAP® GRC Services section to discover how we can help you improve the efficiency and security of your SAP system.