Inprosec a través de sus servicios, como el SAP Security Assessment, ayuda a sus clientes a mejorar los niveles de seguridad de sus sistemas SAP.
Hoy os traemos la actualización de las notas de seguridad de SAP, del Q2 de 2020.
Notas Q2 2020
Resumen y highlights del Trimestre
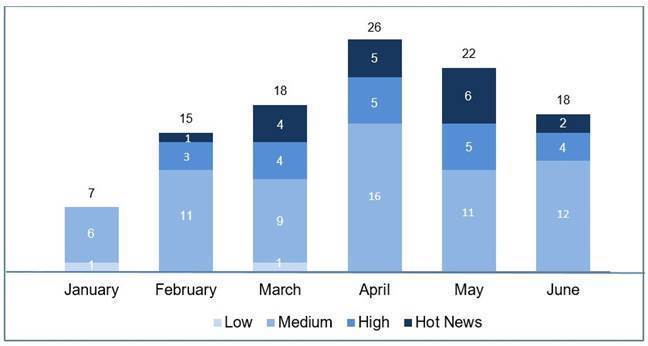
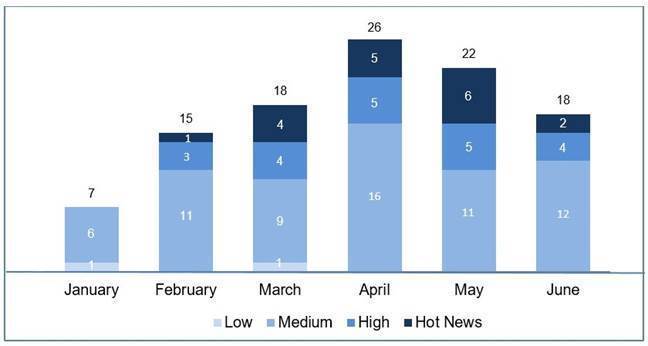
La tendencia que llevábamos de un número menor de notas/parches, en este trimestre y ya desde el mes de Abril se ha invertido, no solo por ser el trimestre con mayor número de notas que de los últimos años, sino el que del mayor número notas críticas que podamos recordar, con un total de 11. Las notas altas también son un número muy significativo, con un total de 17 en el trimestre. En efecto, en esta revisión dejaremos las notas medias sin revisar como siempre, pero incluso excluiremos alguna de las altas de menor CVSS, y a pesar de ello daremos detalle de un total de 22 notas (todas las que tengan un CVSS de 7.5 o mayor), apareciendo una crítica de SAP BO por duplicado al publicarse en Abril y actualizarse en Mayo.
Tenemos 13 notas críticas (Hot News) únicas, siendo el total de 12 en este trimestre, una de ellas la actualización recurrente para el SAP Business Client con Chromium con 1 aparición y una crítica de SAP BO que aparece en Abril y se actualiza en Mayo. Además revisaremos en detalle 9 del total de 17 notas altas (aquellas de CVSS mayor o igual a 7.5) para la revisión en detalle de 22 notas distintas.
- La 2ª nota más crítica del año (CVSS 9.9) relacionada con la inyección de código que afecta a cualquier servidor de aplicación ABAP (ABAP AS).
- Las siguientes en criticidad (CVSS 9.8) son cuatro, una es la habitual “Browser Control Chromium Delivered with SAP Business Client (2622660)” que aparece en Mayo y por 3º vez en el año; y luego tenemos una de SAP BO Business Intelligence Platform en Mayo y dos en Abril; una de Apache Tomcat, que afecta a SAP Liquidity Management for Banking, vulnerabilidad conocida como ”Ghostcat”; y otra para SAP Commerce debido al uso de credenciales por defecto (en cuenta de administrador).
- A partir de ahí, tenemos una crítica con CVSS de 9.0 y otra con 9.3 y el resto (5) se sitúan en un CVSS de 9.1.
- De las de nivel alto quizás debamos destacar que existen 2 para para SAP Solution Manager con CVSS de 8.6 y 8.1 respectivamente.
Tenemos un total de 81 notas para todo el trimestre, 42 más que el pasado trimestre – más del doble, (66 de los patch Tuesday, 36 más que el pasado trimestre):
- En Abril se han publicado un total de 29 notas (26 en el Security Notes Tuesday – 23 nuevas y 3 actualizaciones de notas anteriores), lo que supone el mayor número en un mes en lo que va de año.
- Además tenemos un total de 5 “hot news” (críticas), lo cual no veíamos en un mismo mes desde Diciembre del 2014, centradas en las siguientes plataformas: SAP Portal, SAP Commerce, SolMan y SAP Host Agent. 4 de las notas tienen CVSS de 9.1, pero la más crítica alcanza un CVSS de 9.3
- Existen también 5 notas de criticidad alta (high priority) siendo la más relevante con un CVSS de 8.6 la que afecta SAP Solution Manager (SolMan). El resto son de nivel medio y no las veremos en detalle, aunque cabe destacar que SAP BusinessObjects es la plataforma más afectada este mes, con un total de 8 notas (1 críticas, 2 altas y 5 medias).
- Este mes los tipos más predominantes son “Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)” (7/29 y 7*/26 en patch day) y “Missing Authorization Check” (6/29 y 3/26 en patch day).
- En Mayo se han publicado un total de 29 notas, al igual que el mes pasado record del año (22 en el Security Notes Tuesday – 18 nuevas y 4 actualizaciones de notas anteriores).
- Tenemos un total de 6 “hot news” (críticas), 4 nuevas destacando la de mayor nivel de todo el trimestre con CVSS 9.9, aunque también existe una para SAP BO con CVSS de 9.8. De las dos actualizaciones, una es el gran clásico “Browser Control Chromium Delivered with SAP Business Client (2622660)”, con su CVSS de 9.8, con su 3ª aparición en lo que va de año y la otra es una actualización de la nota crítica de SAP BO de Abril. Un número mayor de notas críticas todavía que el mes pasado, aunque solo tendríamos 4 nuevas.
- Existen también 7 notas de criticidad alta (high priority) la más relevante con un CVSS de 8.8 que mediante SQL Injection permite vulnerar el sistema SAP ASE (Adaptative Server). El resto de notas (16) son todas medias y la plataforma destacada este mes es SAP Adaptative Server Enterprise (SAP ASE) con un total de 7 notas (2 críticas, 3 altas y 2 medias).
- Este mes los tipos más predominantes son “Information Disclosure” (6/29 y 3/22 en patch day) y “Missing Authorization Check” (4/29 y 3/22 en patch day).
- En Junio se han publicado un total de 23 notas (18 en el Security Notes Tuesday – 17 nuevas y 1 actualización de una nota anterior).
- Tenemos un total de 2 “hot news” (críticas), siendo una de Apache Tomcat, que afecta a SAP Liquidity Management for Banking, vulnerabilidad conocida como ”Ghostcat”; y otra para SAP Commerce debido al uso de credenciales por defecto (en cuenta de administrador). Las dos con un CVSS a tener en cuenta de de 9.8.
- Existen también 5 notas de criticidad alta (high priority), siendo la más relevante también para SAP Commerce con un CVSS de 8.6. El resto (16) son notas de nivel medio. La aplicación más afectada este mes ha sido SAP Commerce.
- Este mes los tipos más predominantes son “Missing Authorization Check” (6/23 y 2/18 en patch day) e “Information Disclosure” (4/23 y 3/18 en patch day).
En la gráfica (post Junio 2020 de SAP) podemos ver la evolución y clasificación de las notas de los 3 meses del segundo trimestre del año (2020), además de los 3 meses del pasado trimestre (solo las notas del Sec. Tuesday / Patch Day – by SAP):
Detalle completo
El detalle completo de las notas más relevantes es el siguiente (en inglés):
- Missing XML Validation Vulnerability in SAP Commerce (2904480): SAP Hybris is an eCommerce Java-based platform that provides solutions for B2B and B2C commerce, among others. This vulnerability is present in SAP Hybris with a default configuration and exploitable by a remote unauthenticated attacker. It could potentially allow a malicious agent to read sensitive files and data from the system and even affect availability (in some limited scenarios). SAP has provided patches for both SAP Hybris on-prem implementations as well as SAP Commerce Cloud. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.3 / 10 (CVE-2020-6238).
- Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver (Knowledge Management) (2896682): this vulnerability is a Path Traversal present in SAP NetWeaver Knowledge Management, which is a centralized access point for distributed repositories of files along the systems. It lets users navigate through folders, create, delete files, etc. In all these functionalities, a user can upload files. If unpatched, the system does not sufficiently validate input and therefore may allow a potential attacker to overwrite, delete or corrupt arbitrary files on the remote server. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.1 / 10 (CVE-2020-6225).
- Update 2 to Security Note 2808158: OS Command Injection vulnerability in SAP Diagnostics Agent (2839864): In this latest update, SAP updated the ‘Attachments’ section adding a correction in one of the files attached to the note. If you want to better understand the scope and severity of this vulnerability, you can read previous post regarding the original note (Q3 2019). We can confirm that this latest update is a minor one, that improves attachments for customization of the protection after the patch. Customers who have applied the March fix are protected against critical exploitation of this vulnerability.. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.1 / 10 (CVE-2019-0330).
- Deserialization of Untrusted Data in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (CrystalReports WebForm Viewer) (2863731): This notes appears in April and then it is updated in May. It describes the possibility of a remote command execution caused by a deserialization attack in SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence Platform. Parameters of a specific component can be manipulated in order to inject deserialized content. The provided fix enables data encryption for the traffic between client and server so that it can no longer be read. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.1 / 10 (CVE-2020-6219).
- Code Injection vulnerability in SAP OrientDB 3.0 (2900118): It fixes a Code Injection vulnerability in SAP OrientDB 3.0. SAP OrientDB is a multi-model, graph-based, no-SQL database that SAP acquired from Callidus Software Inc. in 2018. Because an attacker requires authentication and script execution privileges the level vulnerability is not the highest. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.1 / 10 (CVE-2020-6230).
- Missing authentication check in SAP Solution Manager (Diagnostics Agent) (2906994): It fixes a missing authentication check in SAP SolMan, which may allow an attacker to read sensitive information or even access administrative or other privileged functionalities abusing the lack of an authentication check-in a component. This vulnerability, despite being a little bit less critical (CVSS vector-only affects confidentiality), has some similarities with the one patched in SAP Security Note #2890213, HotNews that was previously released in March 2019. Both vulnerabilities allow an unauthenticated attacker to get privileged access to SolMan and, combined with other vulnerabilities, post-exploitation alternatives include critical scenarios for affected customers if attacked. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.6 / 10 (CVE-2020-6235).
- Update to Security Note: Remote Code Execution in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (Crystal Reports) (2861301): While this vulnerability also allows the remote execution of code with an even higher impact on the application’s confidentiality and integrity, unlike #2863731, this vulnerability requires user interaction and therefore the CVSS is lower in this case. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.1 / 10 (CVE-2020-6208).
- Information Disclosure in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (dswsbobje Web Application) (2898077): It fixes an Information Disclosure vulnerability. A non-authenticated user could exploit this vulnerability with CVSS of 7.5 in a certain web application of SAP BusinessObjects in order to gain information that can be then used for further exploits and/or attacks. CVSS v3 Base Score: 7.5 / 10 (CVE-2020-6237).
- Code Injection vulnerability in Service Data Download (2835979): Due to an insufficient input validation in a remote-enabled function module that dynamically generates code, an attacker can take complete control of any SAP NW ABAP system that is connected to a Solution Manager (SolMan) system. Only the fact that an attacker needs a minimum level of authorizations to exploit this vulnerability has prevented it from receiving a CVSS of 10.0. Fortunately, there are no manual steps involved in the provided fix. Strong recommendation in applying the corresponding patch as soon as possible is given. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.9 / 10 (CVE-2020-6262).
- Update – Security Updates for the Browser Control Chromium Delivered with SAP Business Client (2622660): This note addresses multiple vulnerabilities in the third-party web browser control Chromium, which is used in SAP Business Client and is periodically updated based on web browser updates. Since exploits for third-party tools are more common than exploits that are SAP-specific, which tend to be more targeted and selective, it is important to keep this note installed with every update to stay secure. These patches provide support for Chromium version 81.0.4044.92. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.8 / 10
- Missing Authentication check in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (Live Data Connect) (2885244): It describes a scenario that leads to a missing authentication vulnerability. Thanks to the unchanged scope in case of an exploit, the CVSS is “only” 9.8. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.8 / 10 (CVE-2020-6242).
- Code injection in SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (Backup Server) (2917275): SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE) Backup Server does not perform the necessary validation checks for an authenticated user while executing DUMP or LOAD command allowing arbitrary code execution or Code Injection. SAP ASE is one of the SQL database servers supported by SAP business applications. It uses a relational data management model and provides on-premises as well as cloud deployment options. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.1 / 10 (CVE-2020-6248).
- Information Disclosure in SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (Cockpit) (2917090): Under certain conditions SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE) Cockpit allows an attacker to access sensitive and confidential information through local network which would otherwise be restricted. It could be used to get user account credentials, tamper with system data and impact system availability. Some well-known impacts of Information Disclosure are: 1) loss of information and system configuration confidentiality; 2) information gathering for further exploits and attacks. SAP ASE is one of the SQL database servers supported by SAP business applications. It uses a relational data management model and provides on-premises as well as cloud deployment options. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.0 / 10 (CVE-2020-6252).
- SQL Injection vulnerability in SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (2916927): The note provides fixing SQL Injection vulnerabilities that can lead to an escalation of privileges and thus allowing authenticated users to execute commands that they are otherwise not allowed to execute. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.8 / 10 (CVE-2020-6241).
- Information Disclosure in SAP Landscape Management (2903743): A disclosure vulnerability exists in the enterprise edition or standard edition of SAP Landscape Management that would allow an authenticated user with high privilege to obtain privileged access to other systems making those other systems vulnerable to information disclosure and modification. The information disclosed are the credentials. The disclosed information can only be accessed by authenticated users with high privileges (J2EE administrator), but they can escalate their privileges to other systems. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.7 / 10 (CVE-2020-6243).
- Code Injection in SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (XP Server on Windows Platform) (2915585): SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (XP Server on Windows Platform) does not perform the necessary checks for an authenticated user while executing the extended stored procedure. Under certain conditions, the impact of this code injection is that the potential attacker can read, modify and delete restricted data on connected servers. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.0 / 10 (CVE-2020-6243).
- SQL Injection vulnerability in SAP Master Data Governance(MDG) (2908560): The use of an admin backend report from within MDG allows an attacker to execute crafted database queries, exposing the backend database. Some well-known impacts of SQL Injection vulnerability are: 1) Read sensitive data; 2) Execute admin level operations on database. CVSS v3 Base Score: 7.7 / 10 (CVE-2020-6249).
- ‘Ghostcat’ Apache Tomcat AJP Vulnerability in SAP Liquidity Management for Banking (2928570): Due to a known vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, called “Ghostcat,” SAP strongly recommends disabling all ports using the Apache JServ Protocol (AJP Protocol). While the note points out the risk of a remote code execution, the description of the corresponding vulnerability mentions that “AJP connections…can be exploited in ways that may be surprising.” The latter statement, together with the CVSS score of 9.8, should be reason enough to disable all AJP ports. If customers absolutely need the AJP protocol in their scenario, the note recommends to set the required secret attribute in the configuration of the AJP connector. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.8 / 10 (CVE-2020-1938).
- Use of Hard-coded Credentials in SAP Commerce and SAP Commerce Datahub (2918924): It addresses hard-coded user credentials in SAP Commerce and SAP Commerce Data Hub. This problem can be found in many software products because the products use some built-in accounts with publicly known passwords and do not force the administrators to change these passwords during or after installing the application. For example, every SAP Basis person knows the owners of “6071992” or “admin” passwords. SAP has now solved the problem for SAP Commerce and SAP Commerce Data Hub. After applying the patch, a new installation of SAP Commerce will only activate the built-in “admin” account. The installer is forced to maintain an initial password for that account. Other built-in users are still created during installation, but they are inactive until an individual password is set for these accounts. The later rule also applies to all built-in users of SAP Commerce Data Hub. An important fact is that the patches only affect new installations of SAP Commerce (Data Hub). They do not remove default passwords from built-in accounts of existing installations. As one option to achieve this, the note proposes to re-initialize the SAP Commerce installation after applying the patch, an option that likely does not apply to most customers. Therefore, the note also provides a Disabling All Default Passwords for Users Guide to remove the default passwords from all built-in accounts. CVSS v3 Base Score: 9.8 / 10 (CVE-2020-6265).
- Information Disclosure in SAP Commerce (2906366): It fixes an Information Disclosure vulnerability in SAP Commerce. Under a specific configuration of some property values, a malicious user could exploit insecure features of the login-form to gain information that could be used for further exploits and attacks. Some of the required property values are even set by default. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.6 / 10 (CVE-2020-6264).
- Missing XML Validation in SAP Solution Manager (Problem Context Manager) (2931391): It describes a Missing XML Validation vulnerability in Problem Context Manager. While an exploit has only a minor impact on the system’s confidentiality, it can have a serious impact on the system’s availability. CVSS v3 Base Score: 8.2 / 10 (CVE-2020-6271).
- Server Side Request Forgery vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP (2912939): It fixes a vulnerability in the architecture of the batch input process allowing a malicious user to grab user credentials. Although the impact on the system’s integrity, confidentiality and availability is high, the CVSS score is “only” 7.6 as the attack complexity is high and it also needs admin privileges on MS SQL Server as well as batch input authorizations in SAP in order to successfully exploit the vulnerability. CVSS v3 Base Score: 7.6 / 10 (CVE-2020-6275).
Enlaces de referencia
Enlaces de referencia del CERT del INCIBE en relación a la publicación de las notas para los 3 meses de este trimestre:
https://www.incibe-cert.es/alerta-temprana/avisos-seguridad/actualizacion-seguridad-sap-abril-2020
https://www.incibe-cert.es/alerta-temprana/avisos-seguridad/actualizacion-seguridad-sap-mayo-2020
https://www.incibe-cert.es/alerta-temprana/avisos-seguridad/actualizacion-seguridad-sap-junio-2020
Otras referencias, en inglés de SAP y Onapsis (en orden: Julio->Septiembre):
https://wiki.scn.sap.com/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=544214202
https://onapsis.com/blog/sap-security-notes-april-2020
https://wiki.scn.sap.com/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=545396222
https://onapsis.com/blog/sap-security-notes-may-2020
https://wiki.scn.sap.com/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=547426775
https://onapsis.com/blog/sap-security-notes-june-2020
Recursos afectados
- Adobe LiveCycle Designer, versión 11.0;
- SAP Adaptive Extensions, versión 1.0;
- SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise, versiones 15.7 y 16.0;
- SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (Backup Server), versión 16.0;
- SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (Cockpit), versión 16.0;
- SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (XP Server on Windows Platform), versiones 15.7 y 16.0;
- SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (Web Services), versiones 15.7 y 16.0;
- SAP Application Server ABAP, versiones 2008_1_46C, 2008_1_620, 2008_1_640, 2008_1_700, 2008_1_710 y 740;
- SAP Business Client, versiones 6.5 y 7.0;
- SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform, versiones anteriores a la 4.1, 4.2 y 4.3;
- SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform, versiones 4.1, 4.2 y 4.3;
- SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (CMC y BI launchpad), versión 4.2;
- SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (CrystalReports WebForm Viewer), versiones 4.1 y 4.2;
- SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (Live Data Connect), versiones 1.0, 2.0 y 2.x;
- SAP Business One (Backup service), versiones 9.3 y 10.0;
- SAP Commerce, versiones 6.6, 6.7, 1808, 1811 y 1905;
- SAP Commerce (Data Hub), versiones 6.7, 1808, 1811 y 1905;
- SAP Diagnostic Agent (LM-Service), versión 7.20;
- SAP Enterprise Threat Detection, versiones 1.0 y 2.0;
- SAP ERP, versiones 618, 730 y EAPPLGLO 607;
- SAP ERP (Statutory Reporting for Insurance Companies), versiones EA-FINSERV 600, 603, 604, 605, 606, 616, 617, 618 y 800, y S4CORE 101, 102, 103 y 104;
- SAP Fiori for SAP S/4HANA, versiones 200, 300, 400 y 500;
- SAP Fiori Launchpad, versiones 753 y 754.
- SAP Gateway, versiones 7.40, 2.00, 7.5, 7.51, 7.52 y 7.53;
- SAP Host Agent, versión 7.21;
- SAP Identity Management, versión 8.0.
- SAP Landscape Management, versión 3.0;
- SAP Liquidity Management for Banking, versión 6.2;
- SAP Master Data Governance, versiones S4CORE 101; S4FND 102, 103 y 104; SAP_BS_FND 748; y versiones 748, 749, 750, 751, 752, 800, 801, 802, 803 y 804;
- SAP NetWeaver:
-
- Knowledge Management, versiones 7.00, 7.01, 7.02, 7.30, 7.31, 7.40 y 7.50;
- AS (Application Server) Java (HTTP Service), versiones 7.10, 7.11, 7.20, 7.30, 7.31, 7.40 y 7.50;
- AS ABAP, versiones 700, 701, 702, 710, 711, 730, 731, 740, 750, 751, 752, 753, 754, 75A, 75B, 75C, 75D y 75E;
- AS ABAP (Business Server Pages Test Application SBSPEXT_TABLE), versiones 700, 701, 702, 730, 731, 740, 750, 751, 752, 753 y 754;
- AS ABAP (Banking Services), versiones 710, 711, 740, 750, 751, 752, 75A, 75B, 75C, 75D y 75E;
- AS ABAP (Web Dynpro ABAP), versiones SAP_UI 750, 752, 753 y 754; SAP_BASIS 700, 710, 730, 731 y 804;
- SAP NetWeaver AS JAVA (P4 Protocol), versiones:
-
- CORE-TOOLS 7.00, 7.01, 7.02, 7.05, 7.10, 7.11, 7.20, 7.30, 7.31, 7.40 y 7.50;
- SAP-JEECOR 7.00 y 7.01;
- SERVERCOR 7.10, 7.11, 7.20, 7.30, 7.31, 7.40 y 7.50;
- SAP OrientDB, versión 3.0;
- SAP Plant Connectivity, versiones 15.1, 15.2, 15.3 y 15.4;
- SAP S/4 HANA, versiones 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, FSAPPL 400, 450, 500 y S4FPSL 100;
- SAP Solution Manager (Diagnostics Agent), versión 7.2;
- SAP Solution Manager (Problem Context Manager), versión 7.2;
- SAP Solution Manager (Trace Analysis), versión 7.20;
- SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting, versión 2005